Ethical hacking PPT Download 1. Ethical Hacking 2. Ethical Hacking -? Why – Ethical Hacking? Ethical Hacking - Process Ethical Hacking – Commandments Reporting.
<ul><li> Slide 1 </li> <li> 1 Footprinting Scanning Enumeration Isbat Uzzin Nadhori Informatical Engineering PENS-ITS </li> <li> Slide 2 </li> <li> 2 Intelligence Gathering Techniques 3 Major Steps Foot Printing Scanning Enumeration Similar to Military Gather information on the target Analyze weaknesses Construct and launch attack </li> <li> Slide 3 </li> <li> 3 Googling your way insecurity Intittle : welcome to IIS 4.0 to get list of Windows IIS 4.0 server which have had security vulnerabilities and usually easy pickings for attacker VNC Desktop inurl:5800 allows remote users to connect and remote a users desktop Filetype: pwd service to get links reveal several usernames and password </li> <li> Slide 4 </li> <li> 4 Gathering Process Overview You cant attack what you dont know </li> <li> Slide 5 </li> <li> 5 Hacking Step </li> <li> Slide 6 </li> <li> 6 Hacking Step </li> <li> Slide 7 </li> <li> 7 Gathering Process overview Hosts Ports Services Vulnerabilities </li> <li> Slide 8 </li> <li> 8 Footprinting </li> <li> Slide 9 </li> <li> 9 Footprinting Footprinting is the ability to obtain essential information about an organization. Commonly called network reconnaissance. Result Gather information includes: The technologies that are being used such as, Internet, Intranet, Remote Access and the Extranet. To explored the security policies and procedures take an unknown quality and reduce it Take a specific range of domain names, network blocks and individual IP addresses of a system that is directly connected to the Internet This is done by employing various computer security techniques, as: DNS queries nslookup, dig, Zone TransferDNS Network enumeration Network queries Operating system identificationOperating system Organizational queries When used in the computer security lexicon, 'footprinting' generally refers to one of the pre-attack phases; tasks performed prior to doing the actual attack. Some of the tools used for footprinting areSam Spade, nslookup, traceroute, Nmap and neotrace.Sam SpadenslookuptracerouteNmap Ping sweepsPing Point of contact queries Port Scanning Registrar queries (WHOIS queries)WHOIS SNMP queriesSNMP World Wide Web spideringWorld Wide Web </li> <li> Slide 10 </li> <li> 10 Footprinting Steps 1.Determine the scope of your activities 2.Get proper authorization 3.Publicly available information 4.Whois and DNS enumeration 5.DNS interrogation 6.Network reconnaissance </li> <li> Slide 11 </li> <li> 11 DNS Query </li> <li> Slide 12 </li> <li> 12 Network Query Tools * Ping * NSlookup * Whois * IP block search * Dig * Traceroute * Finger * SMTP VRFY * Web browser keep-alive * DNS zone transfer * SMTP relay check * Usenet cancel check * Website download * Website search * Email header analysis * Email blacklist * Query Abuse address </li> <li> Slide 13 </li> <li> 13 Information to Gather Attackers point of view Identify potential target systems Identify which types of attacks may be useful on target systems Defenders point of view Know available tools May be able to tell if system is being footprinted, be more prepared for possible attack Vulnerability analysis: know what information youre giving away, what weaknesses you have </li> <li> Slide 14 </li> <li> 14 OS Identification </li> <li> Slide 15 </li> <li> 15 Point of Contact </li> <li> Slide 16 </li> <li> 16 Tools - Linux Some basic Linux tools - lower level utilities Local System hostnameifconfig who, last Remote Systems pingtraceroute nslookup, dig whois arp, netstat (also local system) Other tools lsof </li> <li> Slide 17 </li> <li> 17 Tools Linux (2) Other utilities wireshark (packet sniffing) nmap (port scanning) - more later Ubuntu Linux Go to System / Administration / Network Tools get interface to collection of tools: ping, netstat, traceroute, port scan, nslookup, finger, whois </li> <li> Slide 18 </li> <li> 18 Tools - Windows Windows Sam Spade (collected network tools) Wireshark (packet sniffer) Command line tools ipconfig Many others </li> <li> Slide 19 </li> <li> 19 Traceroute # traceroute ns1.target-company.com traceroute to ns1.target-company.com (xxx.xx.xx.xx), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 fw-gw (209.197.192.1) 0.978 ms 0.886 ms 0.875 ms 2 s1-0-1-access (209.197.224.69) 4.816 ms 5.275 ms 3.969 ms 3 dallas.tx.core1.fastlane.net (209.197.224.1) 4.622 ms 9.439 ms 3.977 ms 4 atm8-0-024.CR-1.usdlls.savvis.net (209.44.32.217) 6.564 ms 5.639 ms 6.681 ms 5 Serial1-0-1.GW1.DFW1.ALTER.NET (157.130.128.53) 7.148 ms 6.595 ms 7.371 ms 6 103.ATM3-0.XR2.DFW4.ALTER.NET (146.188.240.38) 11.861 ms 11.669 ms 6.732 ms 7 152.63.96.85 (152.63.96.85) 10.565 ms 25.423 ms 25.369 ms 8 dfw2-core2-pt4-1-0.atlas.digex.net (206.181.125.153) 13.289 ms 10.585 ms 17.173 ms 9 dfw2-core1-fa8-1-0.atlas.digex.net (165.117.52.101) 44.951 ms 241.358 ms 248.838 ms 10 swbell-net.demarc.swbell.net (206.181.125.10) 12.242 ms 13.821 ms 27.618 ms 11 ded2-fa1-0-0.rcsntx.swbell.net (151.164.1.137) 25.299 ms 11.295 ms 23.958 ms 12 target-company-818777.cust-rtr.swbell.net (151.164.x.xxx) 52.104 ms 24.306 ms 17.248 ms 13ns1.target-company.com (xxx.xx.xx.xx) 23.812 ms 24.383 ms 27.489 ms </li> <li> Slide 20 </li> <li> 20 Traceroute - Network Mapping cw swb Internet Routers </li> <li> Slide 21 </li> <li> 21 Traceroute - Network Mapping cw swb Internet Routers </li> <li> Slide 22 </li> <li> 22 Traceroute - Network Mapping Firewall DMZ cw swb VPN Internet Routers </li> <li> Slide 23 </li> <li> 23 Traceroute - Network Mapping Firewall DMZ www ftp cw swb VPN Internet Routers </li> <li> Slide 24 </li> <li> 24 Traceroute - Network Mapping Firewall DMZ www ftp cw swb VPN Internet Routers </li> <li> Slide 25 </li> <li> 25 Traceroute - Network Mapping Sun Linux Firewall NT Hosts InsideDMZ www ftp cw swb VPN Internet Routers </li> <li> Slide 26 </li> <li> 26 Traceroute - Network Mapping Sun Linux Firewall NT Hosts InsideDMZ www ftp cw swb VPN Internet Routers Linux 2.0.38 xxx.xx.48.2 AIX 4.2.1 xxx.xx.48.1 Checkpoint Firewall-1 Solaris 2.7 xxx.xx.49.17 Checkpoint Firewall-1 Nortel VPN xxx.xx.22. 7 Cisco 7206 204.70.xxx.xxx Nortel CVX1800 151.164.x.xxx IDS? </li> <li> Slide 27 </li> <li> 27 Domain Name: UWEC.EDU Registrant: University of Wisconsin - Eau Claire University of Wisconsin - Eau Claire 105 Garfield Avenue 105 Garfield Avenue Eau Claire, WI 54702-4004 Eau Claire, WI 54702-4004 UNITED STATES UNITED STATESContacts: Administrative Contact: Administrative Contact: Computing and Networking Services Computing and Networking Services 105 Garfield Ave 105 Garfield Ave Eau Claire, WI 54701 Eau Claire, WI 54701 UNITED STATES UNITED STATES (715) 836-5711 (715) 836-5711 networking@uwec.edu networking@uwec.edu Name Servers: TOMATO.UWEC.EDU 137.28.1.17 TOMATO.UWEC.EDU 137.28.1.17 LETTUCE.UWEC.EDU 137.28.1.18 LETTUCE.UWEC.EDU 137.28.1.18 BACON.UWEC.EDU 137.28.5.194 BACON.UWEC.EDU 137.28.5.194 Whois </li> <li> Slide 28 </li> <li> 28 Scanning [determining if the system is alive] </li> <li> Slide 29 </li> <li> 29 Introduction Scanning can be compared to a thief checking all the doors and windows of a house he wants to break into. Scanning- The art of detecting which systems are alive and reachable via the internet and what services they offer, using techniques such as ping sweeps, port scans and operating system identification, is called scanning. The kind of information collected here has to do with the following: 1) TCP/UDP services running on each system identified. 2) System architecture (Sparc, Alpha, x86) 3) Specific IP address of systems reachable via the internet. 4) Operating System type. </li> <li> Slide 30 </li> <li> 30 Ping Sweeps pingping sweep is a method that can establish a range of IP addresses which map to live hosts.IP addresses ICMP Sweeps (ICMP ECHO requests) Broadcast ICMP Non Echo ICMP TCP Sweeps UDP Sweeps </li> <li> Slide 31 </li> <li> 31 PING SWEEPS ICMP SWEEPS ICMP ECHO request ICMP ECHO reply Target alive Intruder Querying multiple hosts Ping sweep is fairly slow Examples UNIX fping and gping WINDOWS - Pinger </li> <li> Slide 32 </li> <li> 32 Broadcast ICMP Intruder Network ICMP ECHO request ICMP ECHO reply Can Distinguish between UNIX and WINDOWS machine UNIX machine answers to requests directed to the network address. WINDOWS machine will ignore it. </li> <li> Slide 33 </li> <li> 33 PING SWEEPS NON ECHO ICMP Example ICMP Type 13 (Time Stamp) Originate Time Stamp - The time the sender last touched the message before sending Receive Time Stamp - The echoer first touched it on receipt. Transmit Time Stamp - The echoer last touched on sending it. </li> <li> Slide 34 </li> <li> 34 PING Sweeps TCP Sweeps Server Client C(SYN:PortNo & ISN) S (SYN & ISN) + ACK[ C (SYN+!) ] RESET (not active) S(ISN+1) When will a RESET be sent? When RFC does not appear correct while appearing. RFC = (Destination (IP + port number) & Source( IP & port number)) </li> <li> Slide 35 </li> <li> 35 PING Sweeps Depends on ICMP PORT UNREACHABLE message. UDP data gram ICMP PORT UNREACHABLE Unreliable because Routers can drop UDP packets UDP services may not respond when correctly probed Firewalls are configured to drop UDP Relies on fact that non-active UDP port will respond Target System </li> <li> Slide 36 </li> <li> 36 PORT SCANNING Types: TCP Connect() Scan TCP SYN Scan( Half open scanning) Stealth Scan Explicit Stealth Mapping Techniques SYN/ACL, FIN, XMAS and NULL Inverse Mapping Reset Scans, Domain Query Answers Proxy Scanning / FTP Bounce Scanning TCP Reverse Ident Scanning </li> <li> Slide 37 </li> <li> 37 Port Scanning Types TCP Connect() Scan SYN packet SYN/ACK listening RST/ACK (port not listening) SYN/ACK A connection is terminated after the full length connection establishment process has been completed </li> <li> Slide 38 </li> <li> 38 Port Scanning Type TCP SYN Scan (half open scanning) SYN packet SYN/ACK listening RST/ACK (port not listening) We immediately tear down the connection by sending a RESET </li> <li> Slide 39 </li> <li> 39 Port Scanning Type Stealth Scan A scanning technique family doing the following Pass through filtering rules. Not to be logged by the targeted system logging mechanism Try to hide themselves at the usual site / network traffic. The frequently used stealth mapping techniques are. SYN/ACK scan FIN scans XMAS scans NULL scans </li> <li> Slide 40 </li> <li> 40 PORT Scanning Techniques: Random Port scan Slow Scan Fragmentation Scanning Decoy Coordinated Scans </li> <li> Slide 41 </li> <li> 41 PORT Scanning Random Port Scan Randomizing the sequence of ports probed may prevent detection. Slow Scan Some hackers are very patient and can use network scanners that spread out the scan over a long period of time. The scan rate can be, for example, as low as 2 packets per day per target site. Fragmentation scanning In case of TCP the 8 octets of data (minimum fragment size) are enough to contain the source and destination port numbers. This will force the TCP flags field into the second fragment. Decoy Some network scanners include options for Decoys or spoofed address in their attacks. Coordinated Scans If multiple IPs probe a target network, each one probes a certain service on a certain machine in a different time period, and therefore it would be nearly impossible to detect these scans. </li> <li> Slide 42 </li> <li> 42 Operating System Detection Banner Grabbing DNS HINFO Record TCP/IP Stack Fingerprinting </li> <li> Slide 43 </li> <li> 43 Operating System Detection </li> <li> Slide 44 </li> <li> 44 Operating System Detection DNS HINFO Record The host information record is a pair of strings identifying the hosts hardware type and the operating system www IN HINFO Sparc Ultra 5 Solaris 2.6 One of the oldest technique </li> <li> Slide 45 </li> <li> 45 Operating System Detection TCP/IP Finger Printing The ideas to send specific TCP packets to the target IP and observe the response which will be unique to certain group or individual operations. Types of probes used to determine the OS type The FIN Probe, The Bogus Flag Probe, TCP initial sequence number sampling, Dont Fragment bit, TCP initial window, ACK value, ICMP error Message Quenching, ICMP message quoting, ICMP error message Echoing Integrity, Type of service, fragmentation handling, TCP options </li> <li> Slide 46 </li> <li> 46 Firewalking Gather information about a remote network protected by a firewall Purpose Mapping open ports on a firewall Mapping a network behind a firewall If the firewalls policy is to drop ICMP ECHO Request/Reply this technique is very effective. </li> <li> Slide 47 </li> <li> 47 How does Firewalking work? It uses a traceroute-like packet filtering to determine whether or not a particular packet can pass through a packet-filtering device. Traceroute is dependent on IP layer(TTL field), any transport protocol can be used the same way(TCP, UDP, and ICMP). </li> <li> Slide 48 </li> <li> 48 What Firewalking needs? The IP address of the last known gateway before the firewall takes place. Serves as WAYPOINT The IP address of a host located behind the firewall. Used as a destination to direct packet flow </li> <li> Slide 49 </li> <li> 49 Getting the Waypoint If we try to traceroute the machine behind a firewall and get blocked by an ACL filter that prohibits the probe, the last gateway which responded(the firewall itself can be determined) Firewall becomes the waypoint. </li> <li> Slide 50 </li> <li> 50 Getting the Destination Traceroute the same machine with a different traceroute-probe using a different transport protocol. If we get a response That particular traffic is allowed by the firewall We know a host behind the firewall. If we are continuously blocked, then this kind of traffic is blocked. Sending packets to every host behind the packet- filtering device can generate an accurate map of a networks topology. </li> <li> Slide 51 </li> <li> 51 How to identify/avoid threats? Long-standing rule for Unix System administrators to turn off any services that arent in use For personal workstations! Hackers have access to utilities to scan the servers but so do you!. Hackers look in for open ports. So we can our servers first and know what the hackers will see and close any ports that shouldnt be open. </li> <li> Slide 52 </li> <li> 52 Some tools to help us Nmap It is a utility that scans a particular server and informs us which ports are open. Ethereal It is a utility that will scan the network and help us decode what is going on. We can watch the network traffice and find out if hackers can see anything that will help them break into our systems. </li> <li> Slide 53 </li> <li> 53 Enumeration </li> <li> Slide 54 </li> <li> 54 Introduction to Enumeration Enumeration extracts information about: Resources or shares on the network User names or groups assigned on the network Last time user logged on Users password Before enumeration, you use Port scanning and footprinting To Determine OS being used Intrusive process </li> <li> Slide 55 </li> <li> 55 NBTscan NBT (NetBIOS over TC...</li></ul>
What Is Ethical Hacking
- Ethical Hacking Useful Resources
Ethical Hacking Pdf

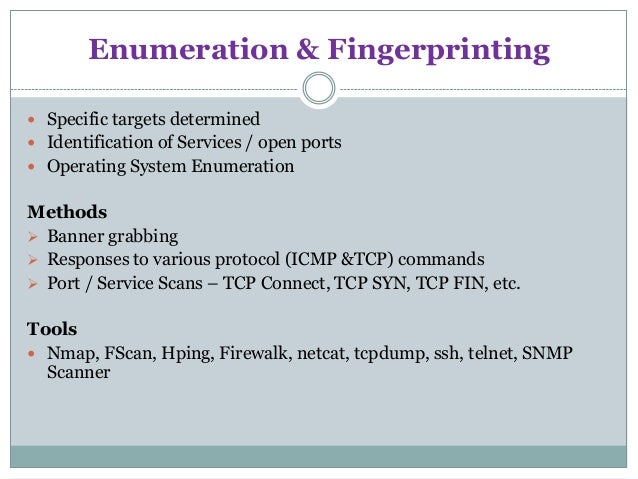
Enumeration belongs to the first phase of Ethical Hacking, i.e., “Information Gathering”. This is a process where the attacker establishes an active connection with the victim and try to discover as much attack vectors as possible, which can be used to exploit the systems further.
Enumeration can be used to gain information on −
- Network shares
- SNMP data, if they are not secured properly
- IP tables
- Usernames of different systems
- Passwords policies lists
Enumerations depend on the services that the systems offer. They can be −
- DNS enumeration
- NTP enumeration
- SNMP enumeration
- Linux/Windows enumeration
- SMB enumeration
Let us now discuss some of the tools that are widely used for Enumeration.
Ethical Hacking Book Download
NTP Suite
NTP Suite is used for NTP enumeration. This is important because in a network environment, you can find other primary servers that help the hosts to update their times and you can do it without authenticating the system.
Take a look at the following example.
enum4linux
Enumeration And Fingerprinting In Ethical Hacking Ppt Slideshare
enum4linux is used to enumerate Linux systems. Take a look at the following screenshot and observe how we have found the usernames present in a target host.
smtp-user-enum
smtp-user-enum tries to guess usernames by using SMTP service. Take a look at the following screenshot to understand how it does so.
Quick Fix
Enumeration And Fingerprinting In Ethical Hacking Ppt Slides
It is recommended to disable all services that you don’t use. It reduces the possibilities of OS enumeration of the services that your systems are running.

